Effect of Iso-Caloric Substitution of Animal #Protein for Other Macro Nutrients on Risk of Overall, Cardiovascular and Cancer Mortality: Prospective Evaluation in EPIC-Heidelberg Cohort and Systematic Review
https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/15/3/794
#Ernährung #Proteine
Recent searches
Search options
#proteine
#Proteine, die #Zellenergie produzieren, in nie dagewesener Auflösung - die Studie von Biologe Florent Waltz und seinem Team an der Universität Basel schafft es auf die Titelseite von #Science.
https://www.snf.ch/de/jwCVwbv7K7SGwdZM/news/hereinzoomen-auf-die-kraftwerke-der-zellen
Ich bin vielleicht ein bisschen angefixt von gebratenem Räuchertofu mit Miso auf Brot
Hier soll es gleich Pizza geben.
Was passt den als Belag auf eine Pizza, um den Proteinanteil zu steigern? – Hefeschmelz allein wird es wohl nicht reißen.
Der Teig aus Dinkelvollkornmehl ist schon fertig…
Mal sehen, was mir noch einfällt. Tipps wären aber prima!
In deze uitzending: Franck Meijboom (Hoogleraar Animal Stewardship, Universiteit Utrecht), Hans Fuchs (Projectleider kennis en innovatie bij Bionext), Sander Verbeek (Eigenaar biodynamisch eierpakstation De Grote Kamp).
Een bio eitje, dat zit wel goed toch?
Daarvoor zullen toch geen eendagshaantjes gedood worden? Een speurtocht naar het verhaal van kip en ei.
Luister aflevering 88 via https://StudioPlantaardig.nl of je favoriete podcast app (Spotify, YouTube, Apple Podcasts etc etc).
Forscher:innen entdecken eine neue Funktion des #Immunsystems und damit einen weiteren möglichen Ansatzpunkt für die Entwicklung neuer #Antibiotika. Sie zeigen, dass das sogenannte Proteasom alte #Proteine in antimikrobielle Moleküle umwandeln kann, wie die BBC berichtet. https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/cpv4jww3r4eo
Het is De Week Zonder Vlees & Zuivel! En naast dit én tal van andere onderwerpen hebben we Maarten Savelberg te gast. In opdracht van @ministerielvvn& @Consumentenbond werd een Burgerpanel duurzame eiwitconsumptie gevormd.
Luister er alles over in het 57e Vegan Journaal!
Den Wandel sähen – wie Europas Landwirte von den Vorteilen pflanzenbasierter #Lebensmittel profitieren können.
Alternative #Proteine schaffen neue Möglichkeiten für #Landwirte, ihr Geschäftsfeld zu erweitern und neue Einnahmequellen zu erschließen. Drei Beispiele aus #Europa.Umfragen zeigen, dass sich eine Mehrheit der Menschen in Deutschland wünscht, dass die Politik Landwirte bei der Umstellung auf einen höheren Anteil #pflanzlicher Lebensmittel unterstützt.
https://gfieurope.org/de/blog/chancen-fuer-landwirte-im-plantbased-sektor/
#plantbased #Ernährung #agrarwende #ernährungswende #Protein #govegan #landwirtschaft
#EU #Leguminosen #Hülsenfrüchte
Forschende weltweit sind überzeugt: #Proteine tragen den Schlüssel zu einer besseren Zukunft in sich. In hochmodernen Laboren entwickeln sie neue, künstliche Proteine, auch solche, die uns gesünder altern lassen. Einige Krankheiten sollen so bald Geschichte sein. Unsere neue #Wissenschaftsdoku - heute um 20.15 Uhr im Programm oder jetzt in der Mediathek: https://www.3sat.de/wissen/wissenschaftsdoku/250123-sendung-die-protein-revolution-wido-100.html?at_medium=Social%20Media&at_campaign=Mastodon&at_specific=3sat
Frans Claes (3x kampioen België + overall wereld kampioen): "Eiwitten? Ik heb daar nooit op gelet."
Luister aflevering 84 (kort & XL) via je
favoriete platform of https://linktr.ee/studioplantaardig
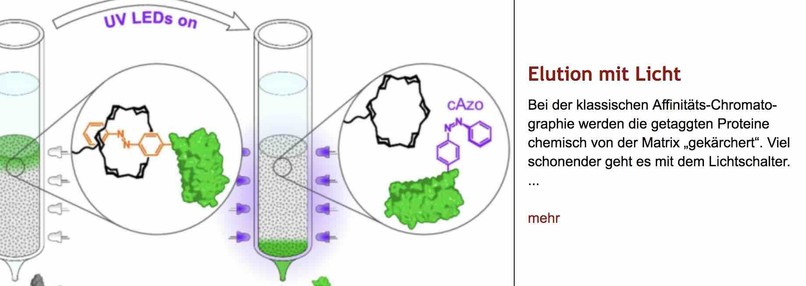
Bei der Affinitäts-#Chromatographie werden die getaggten #Proteine chemisch von der Matrix „gekärchert“. Arne Skerras Gruppe von der TU München löst sie schonender von der Affinitäts-Säule – via Excitographie mit UV-Licht. Andrea Pitzschke erklärt's uns genauer: https://www.laborjournal.de/editorials/3165.php